The Internet has completely transformed our lives, allowing us to connect globally, share ideas, and work remotely. But just as there are threats in the real world, the Internet is also home to cybercriminals who take advantage of vulnerabilities. They use their technical skills to hack into computer systems, steal personal information, and commit financial fraud, among other things.
Unfortunately, Cybercriminals are an ongoing threat, particularly to remote workers who may fall victim to phishing attacks. The dangers posed make understanding how to protect against phishing attacks vital in securing one's digital security.

What is phishing?
You've likely heard the word phishing here and there, but what exactly does it mean? Phishing is when scammers disguise themselves as trustworthy sources to obtain sensitive personal and financial data fraudulently. They employ tactics like misleading emails, fake websites, deceptive text messages (known as smishing), or scam phone calls (known as vishing) to trick individuals into revealing their account credentials and other confidential information.
Remote workers should be concerned about phishing because of their increased digital exposure and vulnerability, especially when working outside secured environments. Understanding this threat and knowing how to prevent phishing attacks is crucial for protecting sensitive data. In this post, we'll highlight important tips and best practices that remote workers can incorporate into their daily routines to stay vigilant and avoid falling victim to malicious phishing attempts.
How to detect phishing attacks
First and foremost, understanding how to identify phishing attempts, learning how to detect phishing attacks, and recognizing common warning signs are crucial to avoid becoming a victim of such scams. Here are some warning signs to be mindful of and how to recognize a phishing attack:
Poor spelling and grammar
Phishing emails and websites often contain typos, grammatical errors, and other style issues. Legitimate companies, on the other hand, will have proper spelling and grammar.
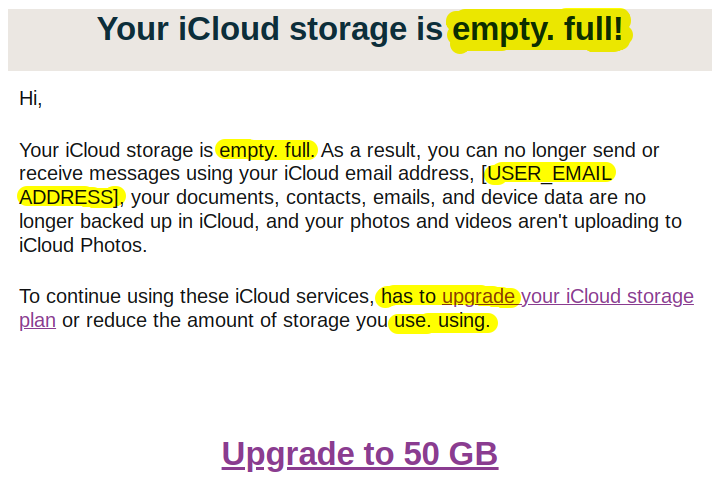
Generic greetings
Phishing emails will use generic greetings like "Dear user," "Dear Sir / Ma'am," or "Dear customer" rather than your actual name.

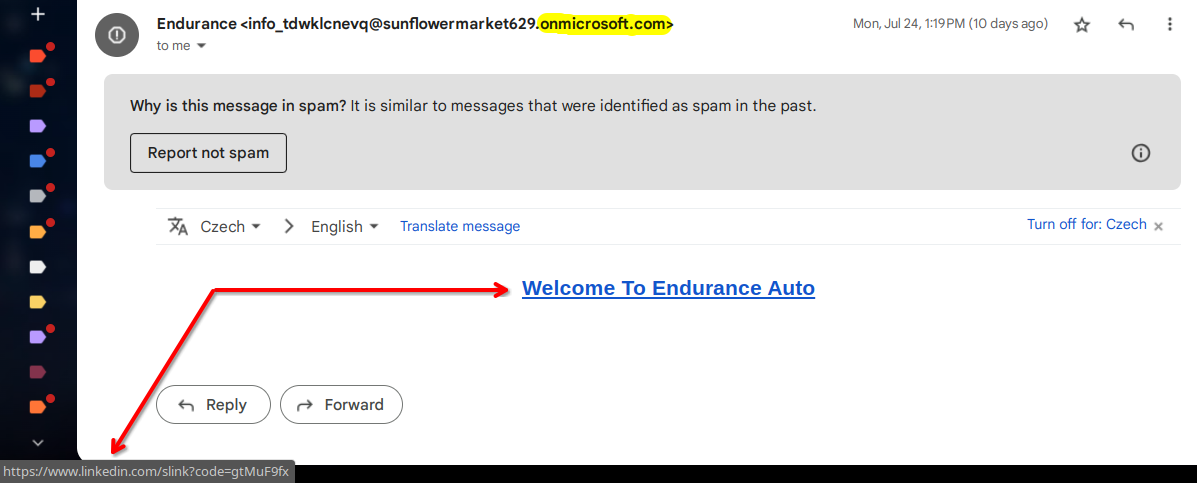
Suspicious links and attachments
Unverified links and attachments in emails or messages can lead to phishing sites or contain malware. For instance, fake links are typical examples of phishing attempts. Never click without verifying first. It's crucial to learn how to detect phishing attacks when dealing with suspicious links in order to protect yourself.
When receiving emails or messages with links, always hover over them before clicking on them. Doing this will reveal the destination URL in a preview pop-up at the bottom of the browser window, allowing you to verify where the link goes before you click it.
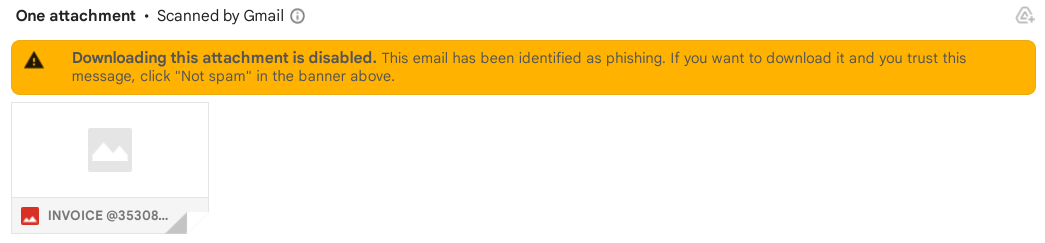
If an attachment seems suspicious, refrain from opening it right away. Instead, contact the purported sender directly using previously known contact information to confirm they sent it. That said, your email provider will sometimes detect a suspicious attachment and block you from downloading it as a safety precaution, so you'll immediately know it's dangerous.
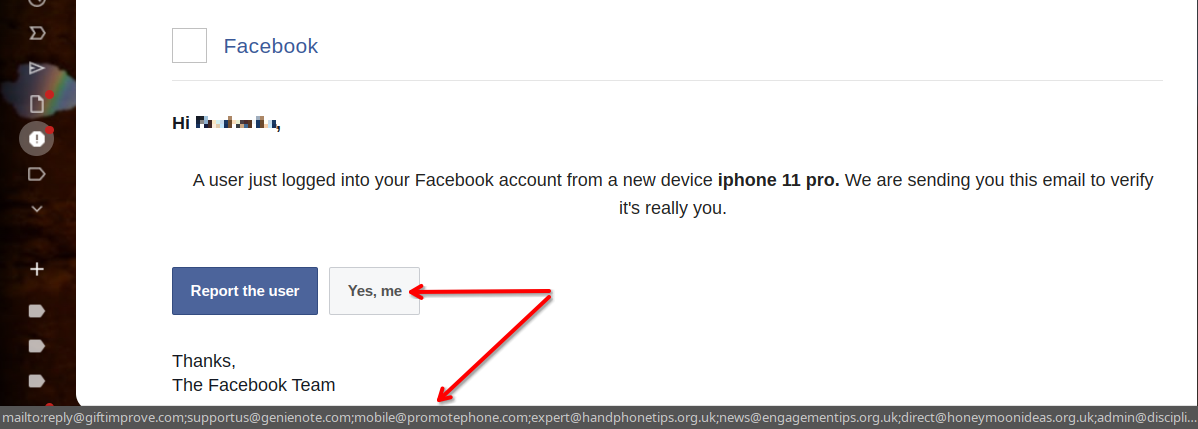
Urgent requests for information
Phishers often create a sense of urgency by pretending a pressing matter requires immediate attention. They might even threaten to suspend your account within a minimal timeframe. Legitimate companies won't resort to such alarming tactics. Instead, they'll give you sufficient time to resolve any issues.

Requests for sensitive information
Reputable organizations won't ask for account passwords, Social Security numbers, or other sensitive data directly through email or messages due to the high risk of data breaches and fraudulent activities. Any requests for this are a huge red flag, and you should verify any highly unusual requests for sensitive information by calling the company directly through a known number—not the contact information provided in the questionable email. By understanding examples of phishing attempts like information requests, you can better learn how to detect phishing attacks.
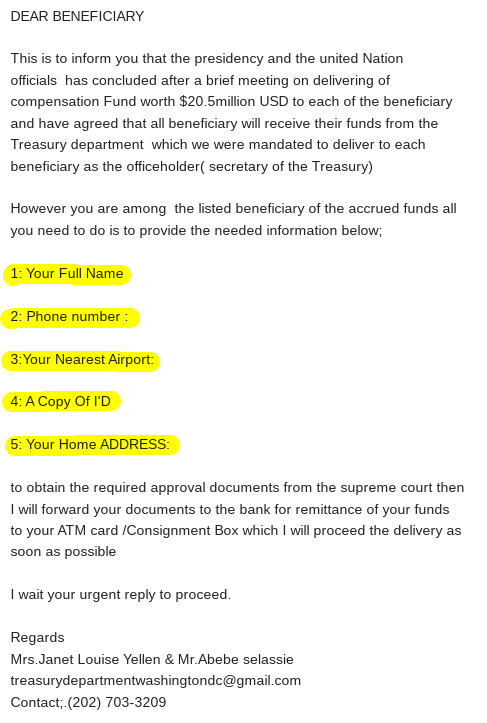
Spoofed email addresses
Look closely at the sender's email address in phishing emails. Scammers often subtly misspell or alter addresses (e.g., amozon.com or paypall.com), which can be hard to notice if you just briefly look over them. Of course, others are more blatantly obvious. Learning how to recognize a phishing attack involves careful inspection, so be sure to do your due diligence.
Lookalike websites
Phishing sites may look nearly identical to real sites to trick users. Always double-check web addresses, branding, and certificates to confirm that sites are legit and secure before entering sensitive data. Some websites may warn you before loading a potential phishing or malware page, but others may not. Understanding examples of phishing attempts like spoofed websites can help you stay secure.
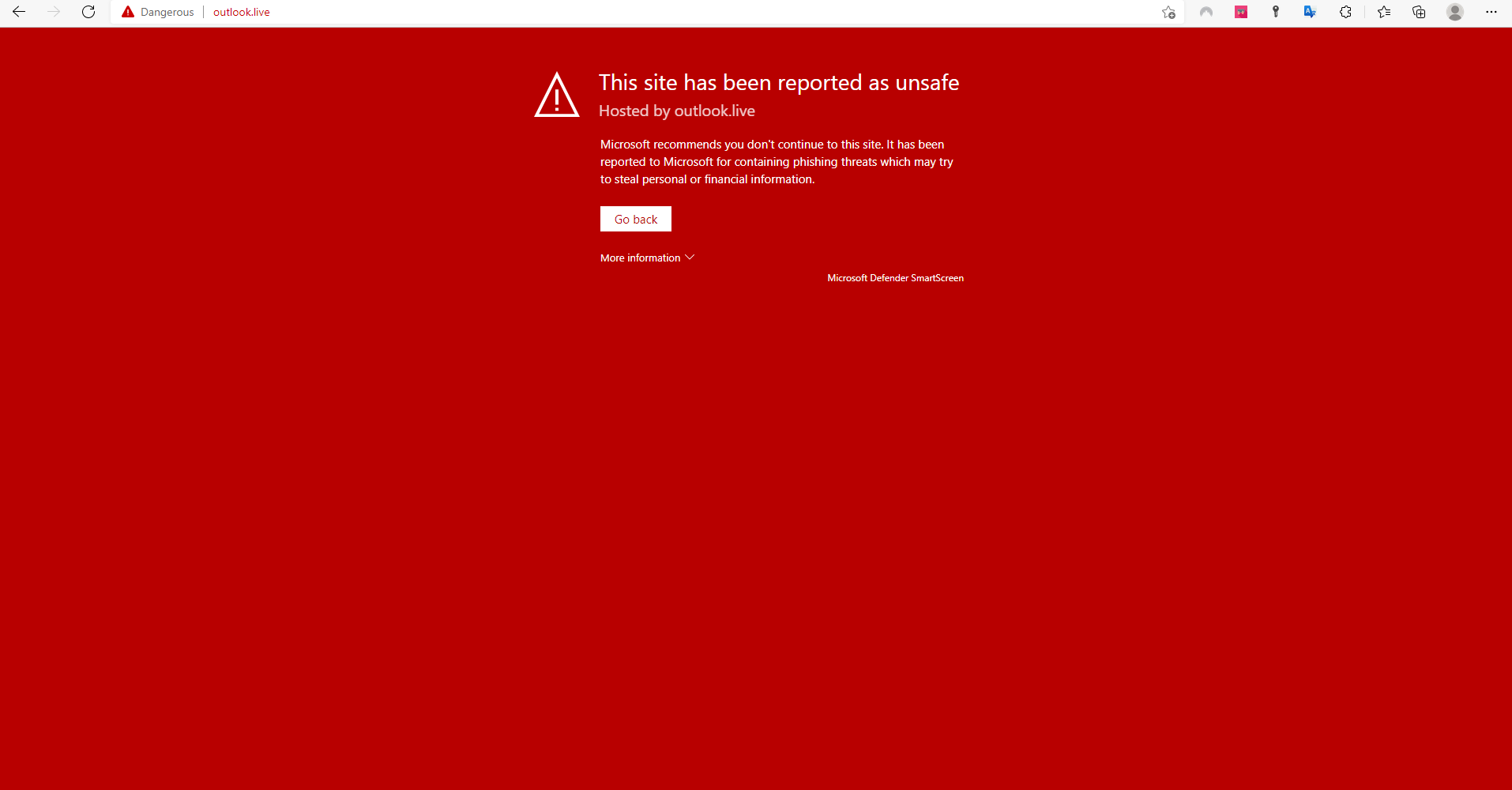
If you're uncertain about the legitimacy of a communication, it's best to directly visit the organization's website by manually typing in their URL. Doing this allows you to verify their website address and contact information. Remember to approach all communications you receive with caution, as paying close attention to each message is critical to maintaining your safety and security online.
How can you avoid phishing attempts?
As you can see, understanding how to protect against phishing attacks and other scams is crucial. Now that you know what these threats entail, it's time to take preventative measures. Here are some best practices for how to prevent phishing attacks:
Always use strong, unique passwords
- Create a unique, complex password for all your accounts, and never reuse the same password. A good rule of thumb is to aim for a minimum of 12 characters and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Avoid using easily guessed information like common words, names (such as significant others, children, and pets), or dates as passwords.
- Change your passwords every 60–90 days or immediately if there's any suspicion of a breach.
Always enable two-factor authentication
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) requires both your password and an additional code to log in, like from an authenticator app or text message. Luckily, more and more services are adding this invaluable security feature.
- Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) helps prevent criminals from accessing your accounts (even if they manage to discover your password) by requiring an additional verification step.
Regularly monitor account activity
- Routinely check bank, credit card, and online account activity for unauthorized transactions, changes, or suspicious login locations.
- Enable login notifications and alerts about account changes for online accounts so you're always in the loop.
Use secure HTTPS websites
- Look for "https:" at the start of website URLs. Websites that start with "http:" are unencrypted and more vulnerable to phishing.
- Browser extensions like HTTPS Everywhere automatically use HTTPS security on sites that support it. Some web browsers also have the option to enable "HTTPS-only" or "HTTPS-first" mode in Settings (here are instructions for Chrome and Firefox).
- Only enter login credentials and sensitive information on HTTPS sites you've verified as legitimate.

Adopting these practices may feel tedious initially, but they're worth the extra time and effort required to protect your online presence. Knowing how to prevent phishing attacks is important, as it is a crucial element of ensuring strong cybersecurity measures. Carefully verifying website security, legitimacy, and connections before entering personal information should become a standard procedure for everyone. Learning how to avoid phishing attempts is critical to protecting yourself online.
What to do if you see a phishing attempt
If you receive an email that seems fishy or is an obvious scam, report it immediately to help protect yourself and others. Here are some recommended ways to report questionable emails and help protect yourself against phishing attacks:
Use your email provider's reporting tools
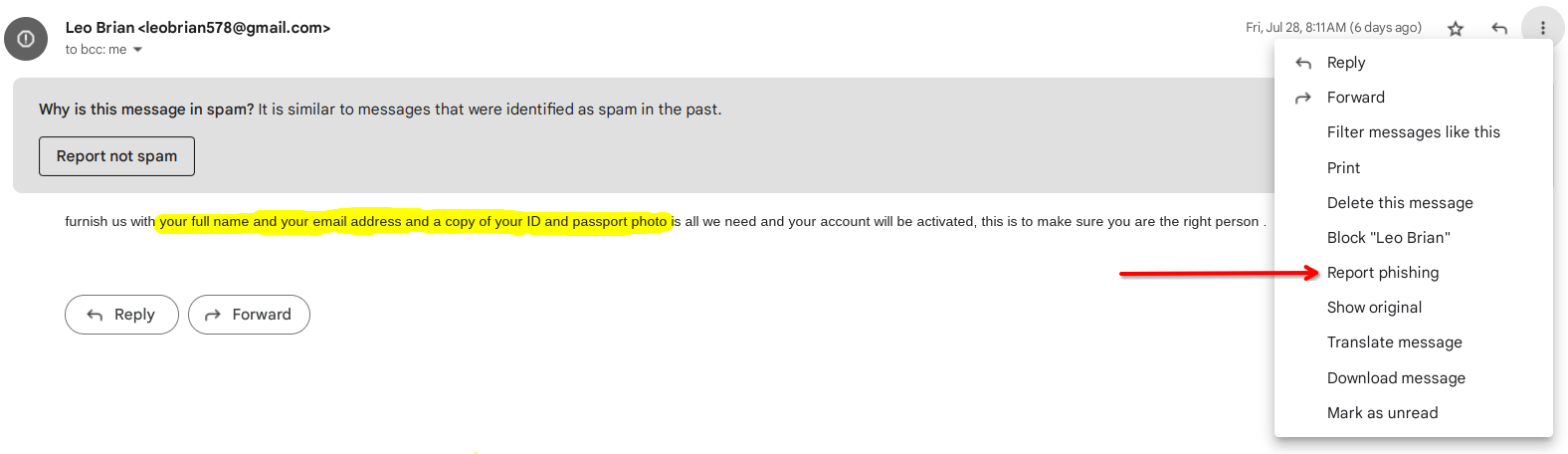
Most email providers have a "Report Phishing" or "Mark as Phishing" option within the email interface (here are instructions for Gmail, Outlook, Apple Mail, and Yahoo). Use this option to report the email as a phishing attempt. It also helps the email service provider identify and block similar scams in the future.
Forward to anti-phishing groups
Forward the suspicious email to groups like the Anti-Phishing Working Group (reportphishing@antiphishing.org) or the Federal Trade Commission (spam@uce.gov). These groups gather scam emails and use them to fight against online fraud.
Contact companies being impersonated
If a scammer is pretending to be a particular brand, forward the phishing attempt to that company's official fraud/security email, if available, or contact their customer support to notify them of the impersonation.
Do not engage with the email
Never reply to a questionable email, click on links within it, or follow any instructions the scammer provides. Doing so could lead to malware, identity theft, or financial loss. Simply report it and delete it. You can avoid potentially dangerous interactions by understanding how to recognize a phishing attack.
By taking a few quick minutes to report suspicious emails through the proper channels, you can do your part in fighting back against phishing scams and cybercrime, thus creating a safer online ecosystem for all. Learning how to recognize and how you can avoid phishing attempts is key to protecting yourself and others online.
Don't get hooked by the phish
No one is safe from the dangers of phishing, especially when it comes to remote workers. However, if you consistently follow these best security practices, stay vigilant, and remain patient, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks.
Understanding how to protect against phishing attacks is essential, and cyber safety should always be our top priority. Learning how to detect phishing attacks, recognizing common examples of phishing attempts, and knowing how to avoid phishing attempts altogether can empower you to steer clear of malicious scams.
